Introduction
CRM software isn’t just a digital address book. It’s the brain of your customer relationships, sitting at the core of how modern businesses sell, market, support, and grow. Whether you’re a business owner trying to scale, a sales director looking for more visibility, or an operations manager frustrated by data silos, understanding where CRM software is used can transform your processes.
In this guide, we’ll break down the real-world applications of CRM systems across departments and industries, showing you not just what CRM can do, but where it matters most. Expect practical examples, use cases, and expert insight designed to help you align your CRM strategy with business goals.
What Is CRM Software?
Definition & Core Functions
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software is a centralised platform that helps businesses manage interactions with current and potential customers. It organises customer data, tracks communications, automates workflows, and enables detailed reporting.
Types of CRMs
- Operational: Streamline sales, marketing, and service processes.
- Analytical: Turn customer data into actionable insights.
- Collaborative: Break down silos between departments for a unified customer experience.
Why Different Departments Use CRM
Sales Teams
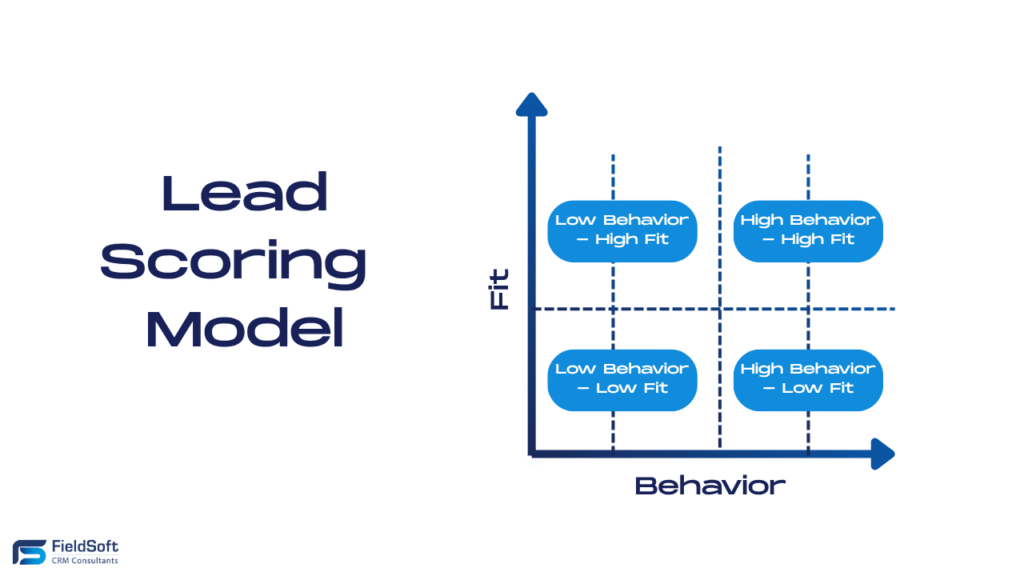
Sales teams use CRM to manage pipelines, prioritise leads, schedule follow-ups, and track performance. Features like lead scoring, contact timelines, and task automation allow reps to focus on closing deals instead of chasing admin.
Marketing
Marketers use CRM to segment audiences, launch automated campaigns, track conversions, and personalise content. When synced with tools like Zoho Campaigns or HubSpot Marketing Hub, CRM becomes a powerful engine for demand generation.
Customer Support
Support teams use CRM to manage tickets, store resolution histories, and track satisfaction metrics. Integrated with help desk software (e.g., Zoho Desk), CRM ensures every agent has full context.
Operations & IT
CRM helps operations track SLAs, maintain data consistency, and align business systems. IT benefits from centralised data architecture and integrations with ERP, finance, and communication tools.
Common Use Cases Across Industries
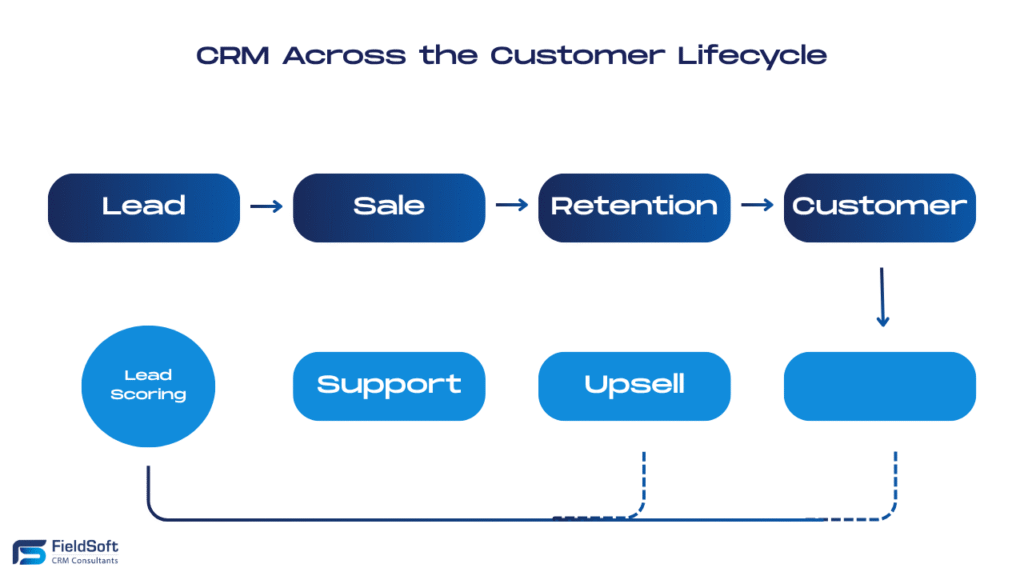
Automating Tasks & Workflows
CRMs reduce manual work by automating repetitive tasks like email follow-ups, quote generation, or task assignment based on deal stage.
Omnichannel Customer Experience
A CRM can unify customer touchpoints—email, phone, web chat, social—into a single timeline, allowing teams to deliver seamless experiences.
Personalised Customer Engagement
Using historical and behavioural data, CRMs allow tailored messaging and content that resonates, whether you’re nurturing a lead or following up post-sale.
Lead Prioritisation & Pipeline Management
CRM systems like Pipedrive and Zoho CRM use scoring algorithms to highlight hot leads, ensuring sales teams focus where the ROI is highest.
Post-Sales Upsell & Churn Prevention
Through renewal reminders, satisfaction tracking, and usage logs, CRM helps teams proactively retain and grow customer accounts.
Industry-Specific Examples
Insurance (Zurich Case Study)
Zurich Insurance integrated AI into their CRM, improving policyholder retention and agent productivity by over 20%.
Construction & Field Services
CRMs like JobNimbus or Zoho CRM FieldTech help track site visits, automate quote approvals, and sync job updates between field and office.
Financial Services & Banking
Highly regulated sectors rely on CRMs with strong compliance features and audit trails. Integration with KYC tools and financial platforms is key.
Legal, Real Estate, Education, Charity
Legal: Manage case pipelines and automate client communication. Real Estate: Track listings, viewings, offers, and contracts. Education: Monitor enrolments and alumni engagement. Charity: Manage donors, campaigns, and volunteer activity.
CRM Software Overview
Market Leaders
- Salesforce: Enterprise-grade, highly customisable.
- HubSpot: Great for inbound marketing and SMEs.
- Zoho CRM: Versatile, scalable, and affordable.
- Microsoft Dynamics: Ideal for organisations using Microsoft 365.
- Pipedrive: Simple and sales-focused.
Key Selection Criteria
- Scalability
- Customisation
- AI capabilities
- Ecosystem integration (e.g., finance, project management)
CRM Features That Matter

Automation & Workflow Tools
Trigger actions like sending emails or assigning tasks based on user behaviour.
Reporting & Analytics
Visual dashboards to track KPIs such as deal velocity, campaign ROI, and customer satisfaction.
AI-Powered Features
Tools like Salesforce Einstein or Zoho Zia predict outcomes, recommend actions, and even write emails.
Integrations & Ecosystem
A CRM’s value grows exponentially when integrated with email, telephony, marketing, help desk, accounting, and ERP.
Measuring CRM ROI
Efficiency & Time Savings
Automations save hours per week, freeing staff for high-value tasks.
Revenue Growth
A CRM reveals which leads convert best, enabling teams to double down.
Customer Satisfaction Metrics
Track NPS, ticket resolution time, and repeat purchases to measure loyalty and retention.
Best Practices for Implementation
Data Strategy & Clean-Up
Avoid “garbage in, garbage out”. Clean data is the foundation of CRM success.
Change Management
Train teams, communicate the “why”, and provide ongoing support.
Cross-Functional Alignment
Ensure marketing, sales, and support work from the same playbook.
Challenges & How to Overcome Them
- Resistance to change: Involve users early and explain benefits.
- Poor data quality: Use validation rules and periodic audits.
- Feature overload: Focus on quick wins, then expand.
Future Trends in CRM Usage
AI Agents & Predictive Analytics
The future is agentic CRM. Systems will predict next best actions, automate them, and learn from results.
Voice-Enabled CRM
CRMs will increasingly support voice input, allowing field reps to update records hands-free.
Quick Takeaways
- CRM software centralises customer interactions across departments.
- Sales, marketing, support, and operations all benefit in unique ways.
- Industry-specific CRMs exist for legal, finance, construction, and more.
- CRM boosts revenue, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
- AI and automation are shaping the next generation of CRM systems.
FAQs
1. Where is CRM software commonly used in business?
CRM is widely used in sales, marketing, customer support, and operations across industries like insurance, finance, construction, and real estate.
2. How do field service teams use CRM software?
They use mobile-friendly CRMs to track jobs, communicate with HQ, and log updates from the field.
3. Can CRM software help prevent customer churn?
Yes. By monitoring satisfaction and renewal dates, CRMs enable proactive engagement to retain clients.
4. What are some examples of AI in CRM?
AI features include lead scoring, predictive deal insights, automatic data entry, and email generation.
5. What is a collaborative CRM?
It focuses on sharing customer data across departments for unified communication and a better customer experience.
Conclusion
CRM software is far more than a tool—it’s the engine of your business’s customer strategy. When used correctly, it empowers sales to close more, marketing to target smarter, support to respond faster, and operations to align better. By understanding where CRM software is used and tailoring its features to your business goals, you move from firefighting to forward planning.
Whether you’re in construction, finance, insurance, or education, there’s a CRM solution that fits. The next step? Audit your current systems, identify the biggest inefficiencies, and see how CRM can plug those gaps.
Need help? FieldSoft offers expert CRM audits and tailored implementations to ensure your CRM delivers real business value.
Reader Engagement Message
We’d love to hear how you use CRM in your business. Which features make the biggest difference? Leave a comment below or share this article with your network to keep the conversation going.
